
Virtual Reality (VR) presents information in a 3-dimensional (3D) form to allow the participate to view the world from inside the world with the ability to interact with the information or world. VR artificially creates a sensory experience, such as light, touch, hearing and smell. The main challenge of VR is tricking the human brain into perceiving digital content as real.
How does VR work?
VR simulation requires two main components: a source of content and a user device, such systems include headsets, all-directions treadmills, special gloves, goggles. The goal of the hardware is to create a virtual environment without the boundaries that are associated with TVs or computer screens, so which ever way you look at the screen mounted to your face follows you.
Using VR in Education
VR can be used at every level of education and has the potential to make a difference. Students can use pre developed applications or can be creative in developing their own virtual worlds.
Advantages
- Visualisation: it can more accurately illustrate some features, processes, allowing extreme close-up examination of an object, observation from a great distance, and observation and examination of areas and events unavailable by other means.
- An alternate method for presentation of material; learning in contexts impossible or difficult to experience in real life.
- motivates students. It requires interaction and encourages active participation rather than passivity. Some types of virtual reality, for example,
- collaboration fostering, using text input with virtual worlds, encourage or require collaboration and provide a social atmosphere.
- allows the learner to proceed through an experience during a broad time period not fixed by a regular class schedule, at their own pace. It allows students with less ability to participate in an experiment or learning environment when they cannot do so otherwise.
- A great potential tool for evaluation and assessment, because of easy monitoring and recording of sessions in a virtual environment.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of using virtual reality are primarily time necessary for learning how to use hardware and software, possible health and safety effects, and cost. Head mounted displays (HMDs) can vary in cost. Higher end HMDs include the Octulus Rift S, which comes with two controllers and comes at a cost of $650. However, there are cheaper alternatives such as Google Cardboard goggles, where students insert their phone.
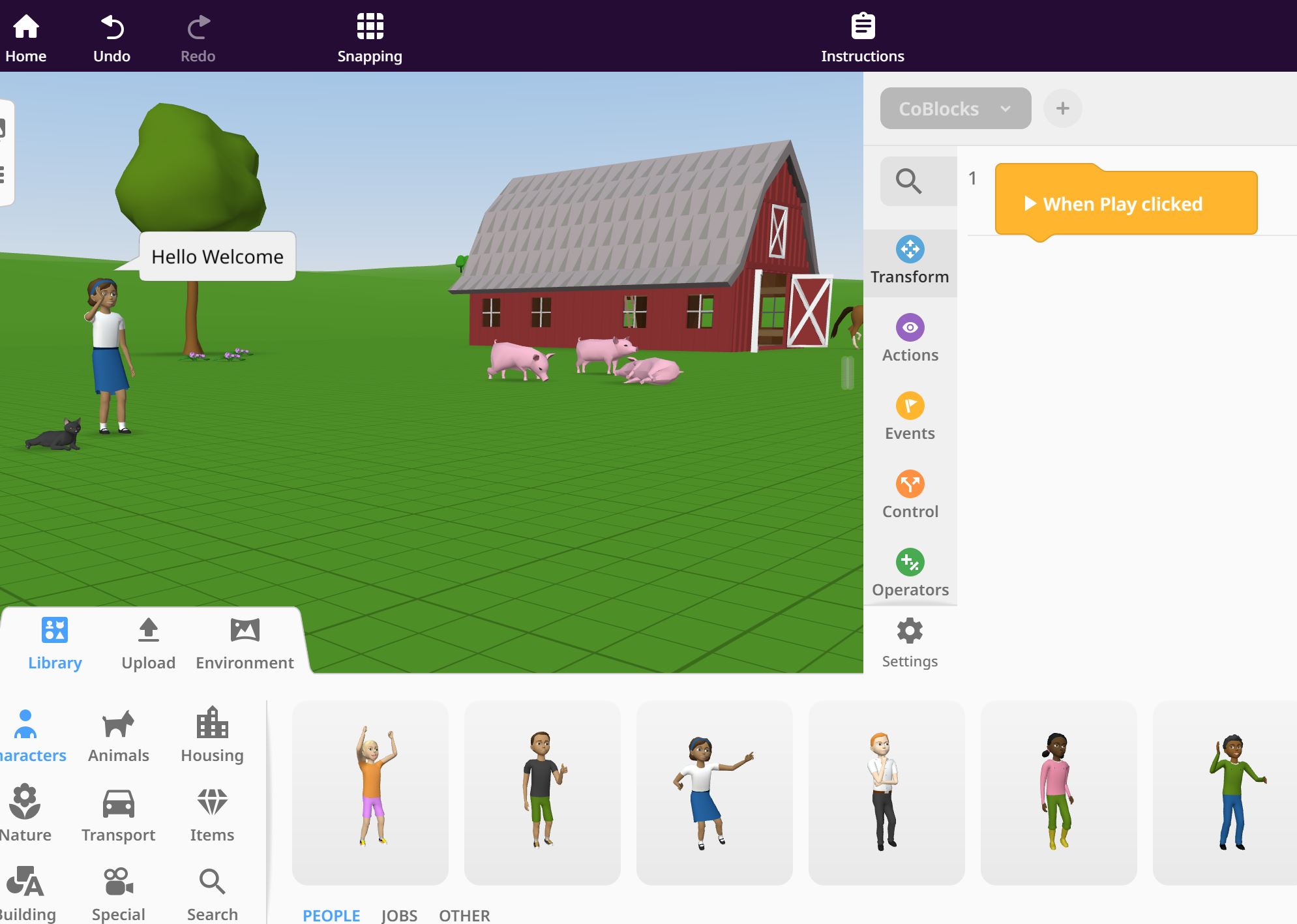
CoSpaces EDU
An application educators can use to encourage creativity through VR. Students can create and share their own virtual world with each other. Backgrounds and objects can be imported from the CoSpace library or by importing their own environment. This application is very easy to use and is suited for all student levels.

References
Pantelidis, V. S. (1995). Reasons to use virtual reality in education. VR in the Schools, 1(1), 9. Retrieved from http://vr.coe.ecu.edu/vrits/1-1pante.htm
Winn, W. (1993). A conceptual basis for educational applications of virtual reality (Technical Report TR-93-9). Seattle, Washington: Human Interface Technology Laboratory, University of Washington. Retrieved from http://www.hitl.washington.edu/publications/r-93-9/
Your blog post on AR was highly informative and I like that you discussed both the advantages and disadvantages. Also a good insight on your experience with CoSpace!
LikeLike
I agree that VR equipment can be expensive, though the Google cardboard is a cheap alternative. The fully immersive gear can be ridiculous, and as you say, require serious training! Using the CoSPaces app in a simple VR glasses setup like cardboard does give a pretty real experience though. It was simple to take the 3D image and import to CoSpaces – I used my driveway – then put a pirate at my front door for protection! School age kids really relate to the familiar environment. It would be easy to have access to any content from there to enable a really engaging lesson! Great introduction to VR!
LikeLike